Engineers at the University of Sheffield (UK) have developed 3D printed mmWave radio aerials (antennas) that could bring stronger mobile phone signals and faster internet connections to remote communities.
Read on to know more about it.
mmWave
Millimeter wave (mmWave) is a type of electromagnetic wave that falls within the millimeter range of the electromagnetic spectrum (hence the name). It has a wavelength between 1 millimeter and 1 meter and a frequency range of 30 GHz to 300 GHz.
These waves are used in a range of applications, including wireless communications, radar, and imaging. They are particularly useful for high-frequency, high-bandwidth applications, such as 5G and 6G mobile networks, as they have a large amount of available bandwidth. However, mmWaves do not travel as far as lower frequency waves, and can be easily blocked by physical objects, so they require line-of-sight and a high density of small cell base stations to provide coverage.
Currently, the aerials (British English for “antennas”) used in telecommunication networks are labor intensive and therefore costly to manufacture when using traditional means. Using the usual methods of fabrication, these aerials can cost hundreds of dollars to manufacture.
The researchers at Sheffield developed their design to be produced cheaper and faster by use of additive manufacturing.
You can see the comparison of the radiation pattern plots produced by the old and new aerials in the image below. This shows how the new printed aerials are almost identical in terms of performance when compared to aerials manufactured the old way. As you can see, the gain and time domain response of the 3D-printed antennas is almost indistinguishable from those manufactured traditionally.
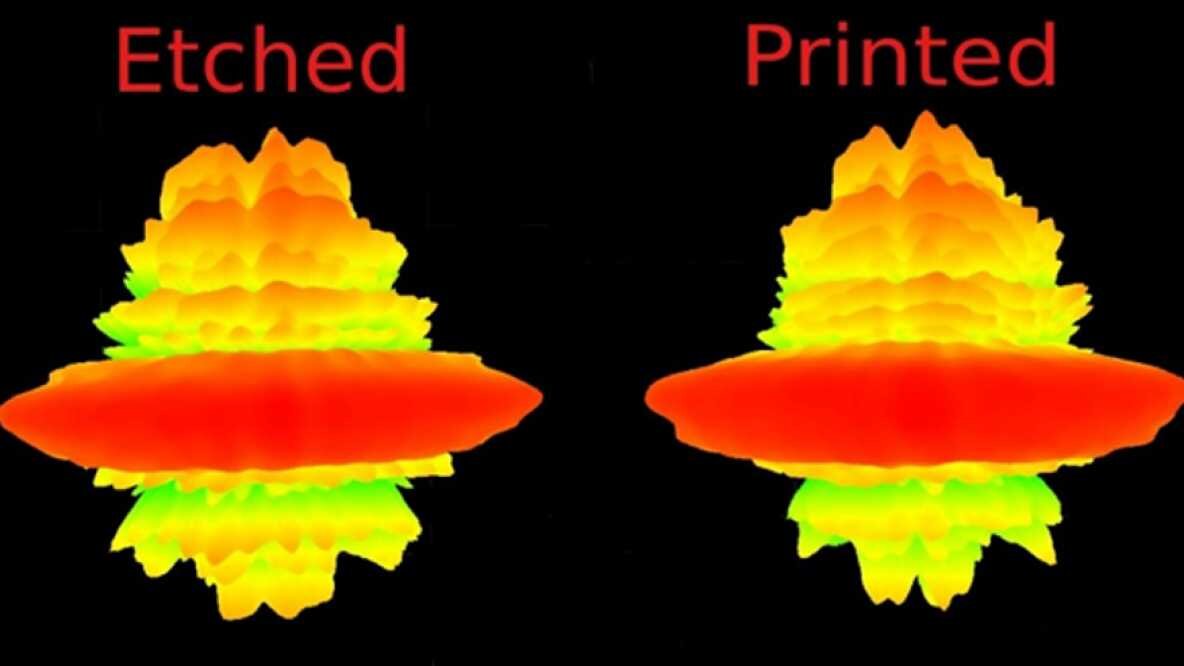
The has developed and produced the antenna that can be produced quickly and inexpensively while still providing comparable performance to traditional antennas.
Conductive Silver
These printed antennas were designed and fabricated by the University’s Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. They were printed using silver nanoparticles, which possess exceptional electrical characteristics.
Although the original source does not specify the exact 3D printing method used to create these antennas, there are several options available for printing with silver nanoparticles, such as extrusion methods, direct ink writing (DIW), and jetting processes.
The use of silver nanoparticles allows for the rapid and cost-effective production of high-performing antennas, which could have important implications for the telecommunications industry.
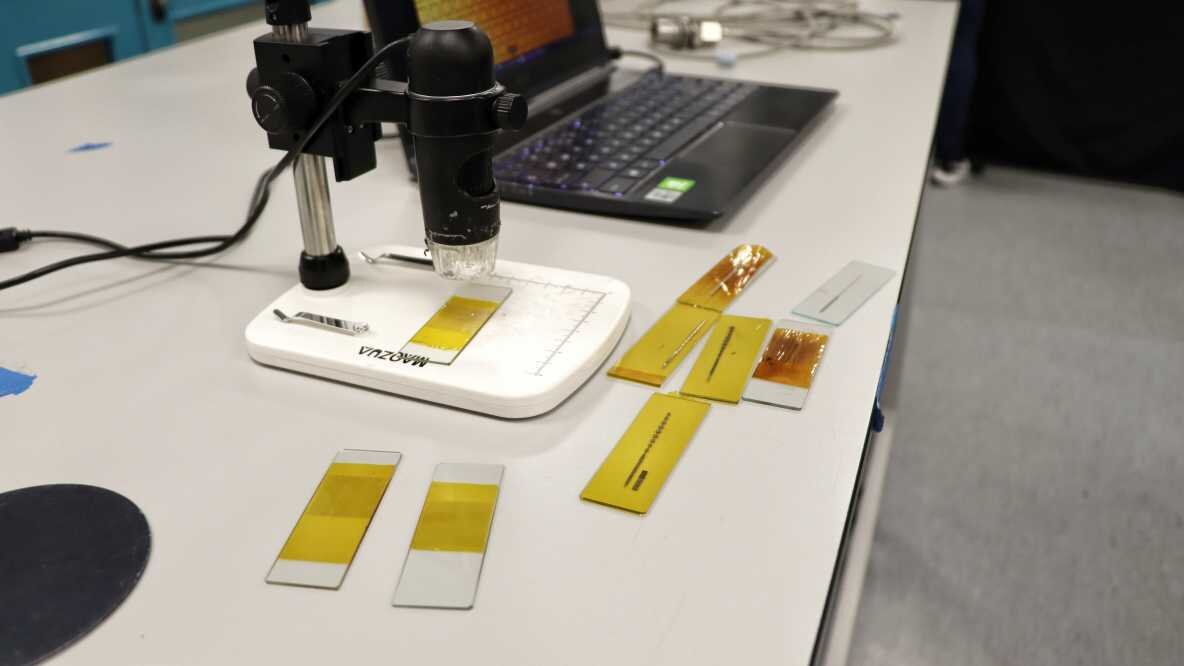

They have been tested at a range of frequencies used by 5G and 6G networks at the university’s UKRI National mmWave Measurement Lab, which can measure systems on chip and antennas up to 110GHz.
The quick and cheap means of producing the antennas means that not only will they become more accessible, but will allow quicker iterations by researchers looking to improve the designs.
“This 3D-printed design could be a game changer for the . It enables us to prototype and produce antennas for 5G and 6G networks at a far lower cost and much quicker than the current manufacturing techniques,” said Eddie Ball, researcher at the Communications Research Group,University of Sheffield.
“The design could also be used to produce antennas on a much larger scale and therefore have the capability to cover more areas and bring the fastest mobile networks to parts of the world that have not yet had access.”
This method could greatly accelerate the development of new 5G and 6G infrastructure.

