New York-based company 3DBio Therapeutics has announced the successful implant of a 3D printed ear onto a patient suffering from microtia, a condition that causes the ear to remain small and undeveloped.
The ear was bioprinted using cells from the patient’s own cartilage to create a biocompatible ear for implanting.
Let’s take a look at the before and after image and then take a look at this medical first.
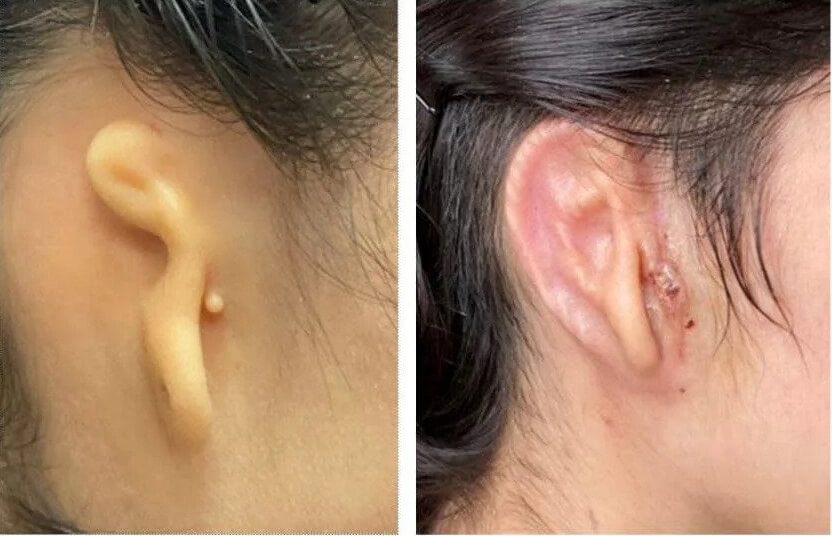
The implant is the first in a set of human trials for patients with microtia and the research is conducted alongside the Microtia-Congenital Ear Deformity Institute.
According to the company, the implant (named “AuriNovo™”) is a patient-matched, 3D-bioprinted living tissue ear implant specifically for microtia patients. Apparently microtia, which often happens in one ear only, is a condition that has very few options for reconstructive surgery, and so bioprinting has been identified as a solution.
There have been previous 3D printed ear implants, but they have previously used
polymers (porous polyethylene (PPE)) as the structure. The AuriNovo trial is the first in the world to use cartilage printed from the users own cells.
Before additive manufacturing came along, typical solutions would involve rib cartilage grafting, which while is beneficial from a biocompatibility point of view, requires a lot of harvesting of rib cartilage, often requiring grafting from up to three ribs.
The procedure starts with a 3D scanning of the patient’s opposite ear to accurately mirror the patient’s ear geometry to form a new full-sized ear. Then a collagen hydrogel scaffold is printed with the company’s custom printer. The patient’s own auricular cartilage cells are integrated into the scaffold, creating a full-sized living ear, ready for transplant onto the patient.
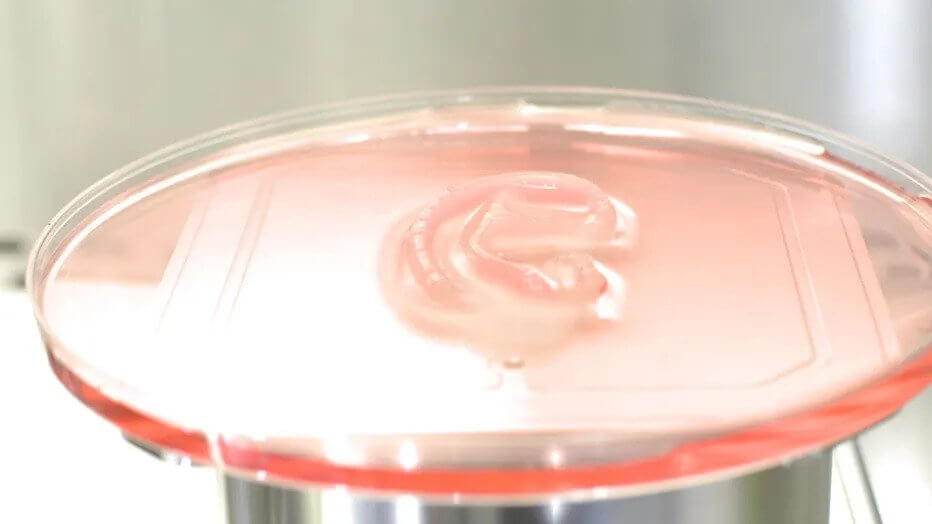

For those who are curious as to what bioprinter they used, it was an in-house designed system dubbed as the GMPrint 3D-bioprinter. Apparently research grade printers lack the requirements for FDA certification, and so the 3DBio Therapeutics built their own.
Their printer enables a fast, high quality and sterile workflow ,and features an AI-based print-path planning algorithm to optimize tool paths for complex materials and geometries.
“As a physician who has treated thousands of children with microtia from across the country and around the world, I am inspired by what this technology may mean for microtia patients and their families,” said Dr. Arturo Bonilla, founder of the Microtia-Congenital Ear Deformity Institute, and surgeon who conducted the implant operation.
“This study will allow us to investigate the safety and aesthetic properties of this new procedure for ear reconstruction using the patient’s own cartilage cells. My hope is that AuriNovo will one day become the standard-of-care replacing the current surgical methods for ear reconstruction requiring the harvesting of rib cartilage or the use of porous polyethylene (PPE) implants.“
“The AuriNovo implant requires a less invasive surgical procedure than the use of rib cartilage for reconstruction. We also expect it to result in a more flexible ear than reconstruction with a PPE implant.”
The study started in August 2021 with this first implant surgery occuring back in March this year. There are 11 patients in the trial according to the company press materials,
“This is a truly historic moment for patients with microtia, and more broadly, for the regenerative medicine field as we are beginning to demonstrate the real-world application of next-generation tissue engineering technology.” said Daniel Cohen, 3DBio Therapeutics Chief Executive Officer and Co-founder.
Indeed, this world first paves the way for living implants for a range of ailments, and the company has its eye on other conditions involving spinal degradation and nasal defects.
Exciting times ahead, and it’s exciting to see bioprinting finally beginning to live up to the hype.


