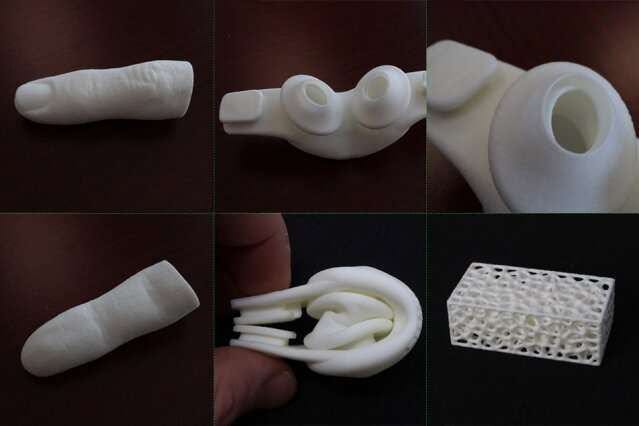
MIT’s Inkbit start-up is using machine learning to produce designs previously deemed impossible. The use of machine learning and machine vision allow the printer to monitor and correct prints at incredible accuracies. It also allows for novel materials and contactless printing without rollers and scrapers.
“The company was born out of the idea of endowing a 3-D printer with eyes and brains,” says Inkbit co-founder and CEO Davide Marini. “Our machine is the first one that can learn the properties of a material and predict its behavior. I believe it will be transformative, because it will enable anyone to go from an idea to a usable product extremely quickly. It opens up business opportunities for everyone.”
Inkbit’s Printers use a vision system to comprehensively scans each layer of the object it is printing to correct errors in real-time. Simultaneously, the machine learning system utilises this information to predict warping of materials and boost the accuracy of the final products. The company claims its machines can print more flexible materials at higher accuracies than other printers.
Machine Learning & Additive Manufacturing
https://youtu.be/FQe2Q3W2ETQ
Another advantage of the machine learning is its ability to adapt to versatile situations. For example, with objects such as computer chips or similar electronics, the machine can precisely print materials around it. The AI can thus work around parts, creating things like casings and packaging. It can even keep a digital replica that can be used for quality assurance, once the print is complete.
Inkbit’s printers are still in the early stage, with currently has just one operational production-grade printer. However, the company will start selling printed products later this year. They have already started a pilot program with Johnson and Johnson. It’s easy to see why industrial partners may be interested in Inkbit’s technology.
In particular, the machine learning and accuracy these printers provide can allow their industrial partners to print some very difficult to print materials. Silicone or high-temperature materials like epoxy are often prone to clogging, but not with this printer. Machine-vision and machine-learning systems provide constant correction and further expand the range of materials the company is able to print by removing the rollers and scrapers used by some other printers to ensure precision. As they tend to jam in conjunction with difficult-to-print materials, this arrangement prevents such errors.
Inkbit’s current industrial printer uses 16 print heads to create multimaterial parts. The machine also uses a contactless inkjet design means increasing the size of later iterations will be as simple as expanding the print block. A proprietary system for mixing two materials before printing will be available on the printers Inkbit ships next year.
Featured image and video Courtesy of Inkbit.