Researchers from the University of Stuttgart have been experimenting with hygromorphic smart structures as passive systems for generating movement in various applications. Hygromorphic means that they change shape when the structures come into contact with water, or in this case, when the humidity changes in the environment.
Read on for more information.
Humidity Responsive
Generally, material limitations hinder the reliability and repeatability of humidity-responsive actuation. The authors of the paper have proposed a codesign method for 4D printing hygromorphic structures using biobased cellulose-filled filaments with varying stiffness and hygroresponsiveness, and have designed mesoscale structuring in printed elements.
The research team successfully designed, fabricated, and tested 4D printed prototypes that can transform in response to relative humidity, with fast, reversible, and repeatable motion in numerous cycles.
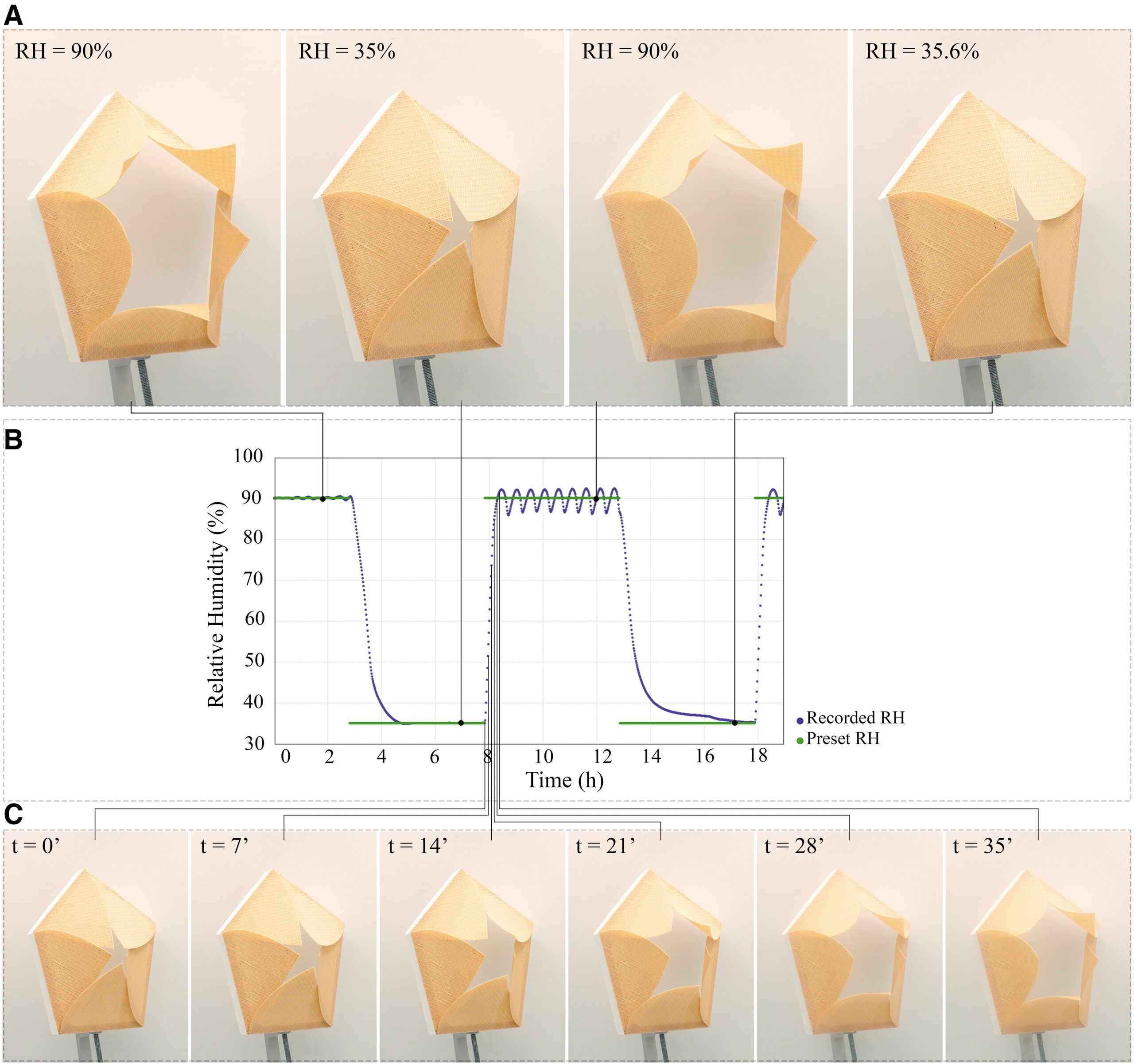
The structures were able to alter their shape within a matter of minutes, in conditions of 35–90% relative humidity (RH), which corresponds to naturally occurring shifts in RH in daily and seasonal weather cycles. This means that the structures can actuate when the weather changes, which can be beneficial for providing shade or shelter for building inhabitants when the weather changes.
You can see one of the printed structures in the image below. The graphic shows the petals of the structure opening as the RH is stepped up over time.
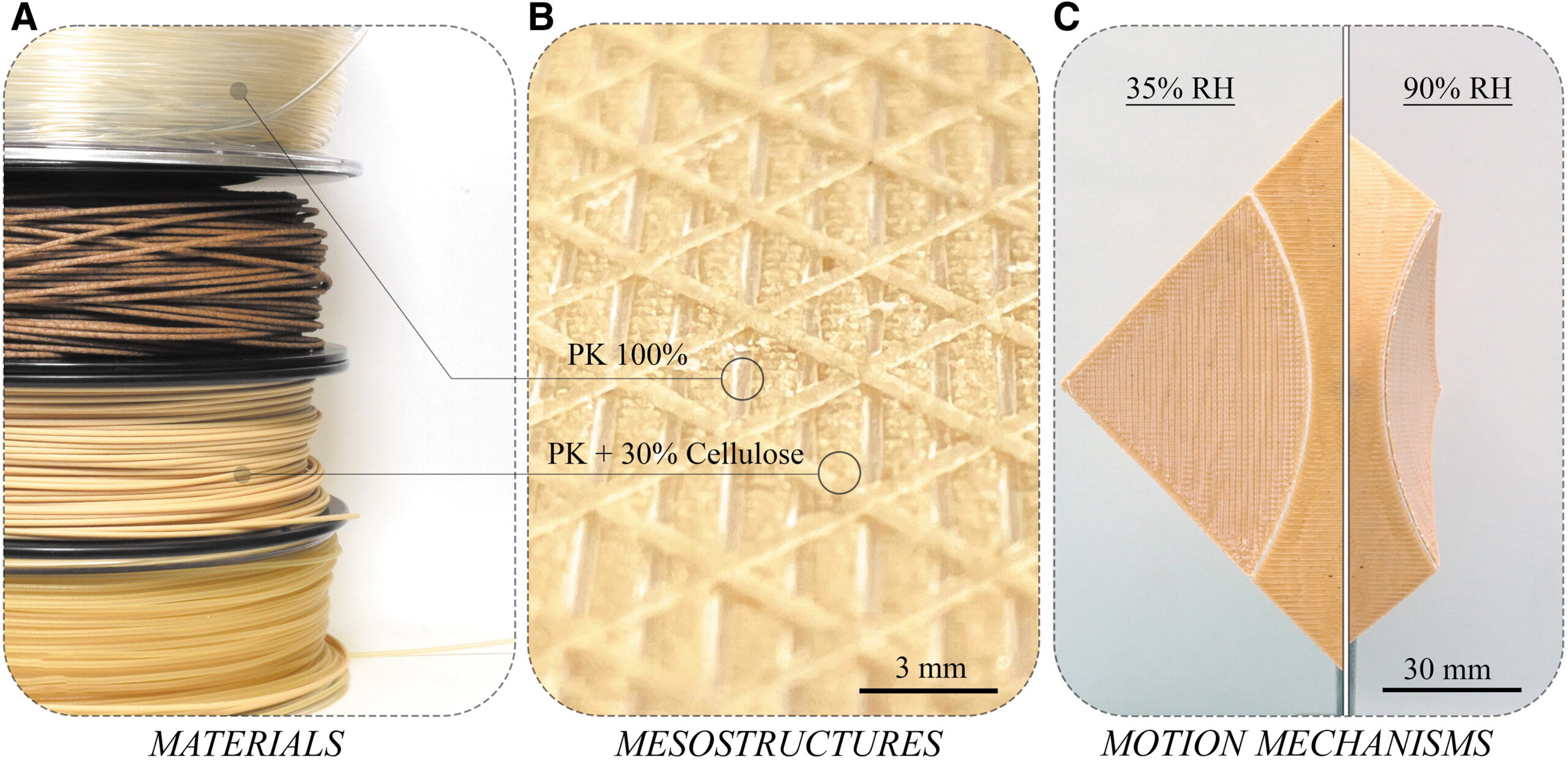
For the 4D structures, the research team produced biocomposite filament materials by compounding native cellulose powder and two partially biobased thermoplastic matrix polymers.
The three-step process involved drying the materials, producing granules by compounding, and extruding them into filaments with a constant diameter of 1.75 mm. The dimensional accuracy of the produced filaments was ensured by continuous measurement with a laser micrometer and wiremaster.
You can see a closeup of one of the printed components, its composition, and the actuated part in the image below.
How it Works
The structure works due to a functional bilayer scheme, which consists of a hygroscopic active layer printed with cellulose-filled filaments and a moisture-stable restrictive layer printed with pure polymers. Many readers will know that plastics can be a little hygroscopic, and this normally negative aspect was utilized as a feature in this design work. The plastic matrix in these experiments consisted of PK and TPU polymers.
An optional bonding layer can also be added to hold the restrictive layer between two compatible material layers, preventing global layer delamination. The toolpath design parameters were adjusted to tune the mesostructural anisotropy and porosity to physically program the shape-change in bilayer constructs.
The bending curvature was controlled through variations in the thickness of layers and filling ratio of the restrictive layer.
The researchers conclude that given the fast response time of the actuation, as well as the range of relative humidity that the actuation occurs in, this method can be used to produce 4D-printed smart structures in weather-adaptive architectural building skins. For example, structures made with this method can open in high RH conditions (usually during fall/winter or at nights), and close to provide shading in low RH conditions (usually in the hot summer time).
You can read the full paper, titled “Codesign of Biobased Cellulose-Filled Filaments and Mesostructures for 4D Printing Humidity Responsive Smart Structures” over at this link.
Come and let us know your thoughts on our Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn pages, and don’t forget to sign up for our weekly additive manufacturing newsletter to get all the latest stories delivered right to your inbox.










