Researchers led by Mejia et al. have developed a real-time monitoring and control system for direct ink write (DIW) 3D printing of thermosetting polymers. The system addresses challenges in controlling the polymerization process during printing, particularly for thermosets that cure through frontal polymerization mechanisms. Their findings were published in npj Advanced Manufacturing.
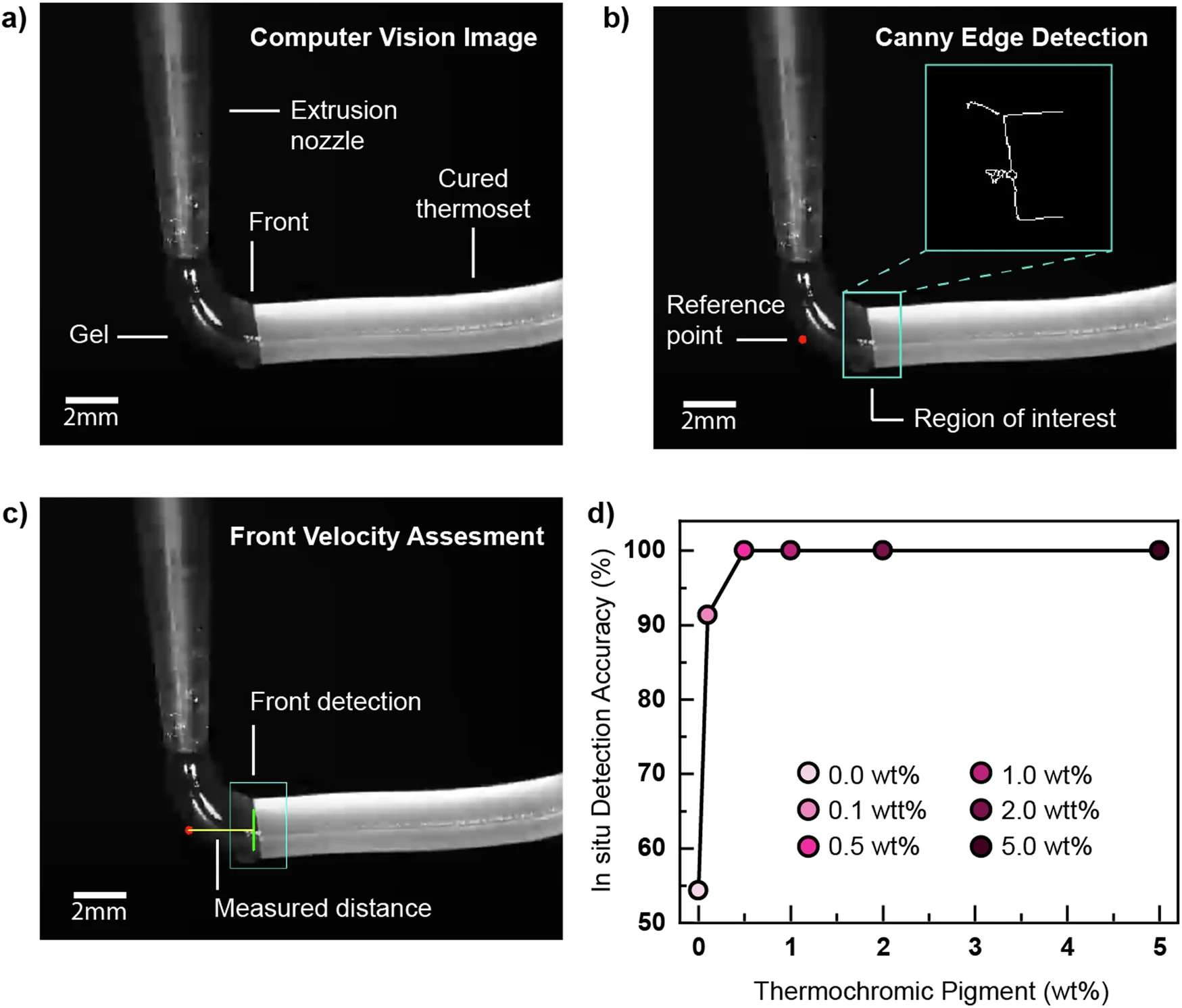
The system combines infrared thermography and optical sensors to monitor the curing process as it occurs. Infrared thermography provides temperature mapping to detect regions undergoing exothermic polymerization, while optical sensors track changes in material translucency or color that correlate with conversion rates. This data feeds into a closed-loop control system that adjusts printing parameters such as ink extrusion rate, deposition temperature, and printer head velocity in real time.
The technology incorporates machine learning algorithms to predict and respond to the polymerization front’s progression. Traditional control systems rely on predetermined thresholds, which the researchers note are inadequate for handling the variable nature of frontal polymerization. The adaptive control system aims to reduce print times and material waste while improving material consistency.
Testing was conducted on acrylate-based thermoset inks commonly used in industrial DIW processes. The researchers compared printed prototypes against traditionally cured samples through mechanical testing, thermal analysis, and microscopy. Results showed improvements in curing uniformity, mechanical strength, and dimensional accuracy compared to conventional methods.
The system is designed with off-the-shelf components and open-source software frameworks for integration into existing industrial 3D printers. The researchers indicate their sensor assembly and control algorithms can be adapted for other material systems undergoing thermally activated reactions, including thiol-ene click chemistries and epoxy-based networks. The modular design aims to support broader adoption across different thermosetting polymer applications.
Source: scienmag.com

