Reliance of fossil fuel based plastics is of growing concern for a number of reasons, not least because oil reserves are finite, and because plastics made from oil have a tendency not to biodegrade.
This is why researchers are looking for new means of producing plastics that use other resources, or else biodegrade, and reduce landfill volume. Many researchers are looking at bio-based plastics to reduce the dependence on petroleum products for manufacturing, as we saw with the durian and pineapple based biocomposites that we saw recently.
A team of researchers from Texas A&M University and the University of Kashmir have found a solution to speed up the biodegrading process that does not rely on plant waste, and instead have elected to use salt and CO2 in their printing process.
Read on to learn more.
Microplastics
When big chunks of plastic break down, they often leave microplastics in their wake. So while it may seem they have disappeared, they really haven’t. The polymers chains in those microplastics hang around indefinitely, and the microplastics can carry heavy metals, bacteria, and even fecal matter in them. This makes them not only gross, but harmful to the environment, and everything else in the food chain that inhabits it. And that includes us.
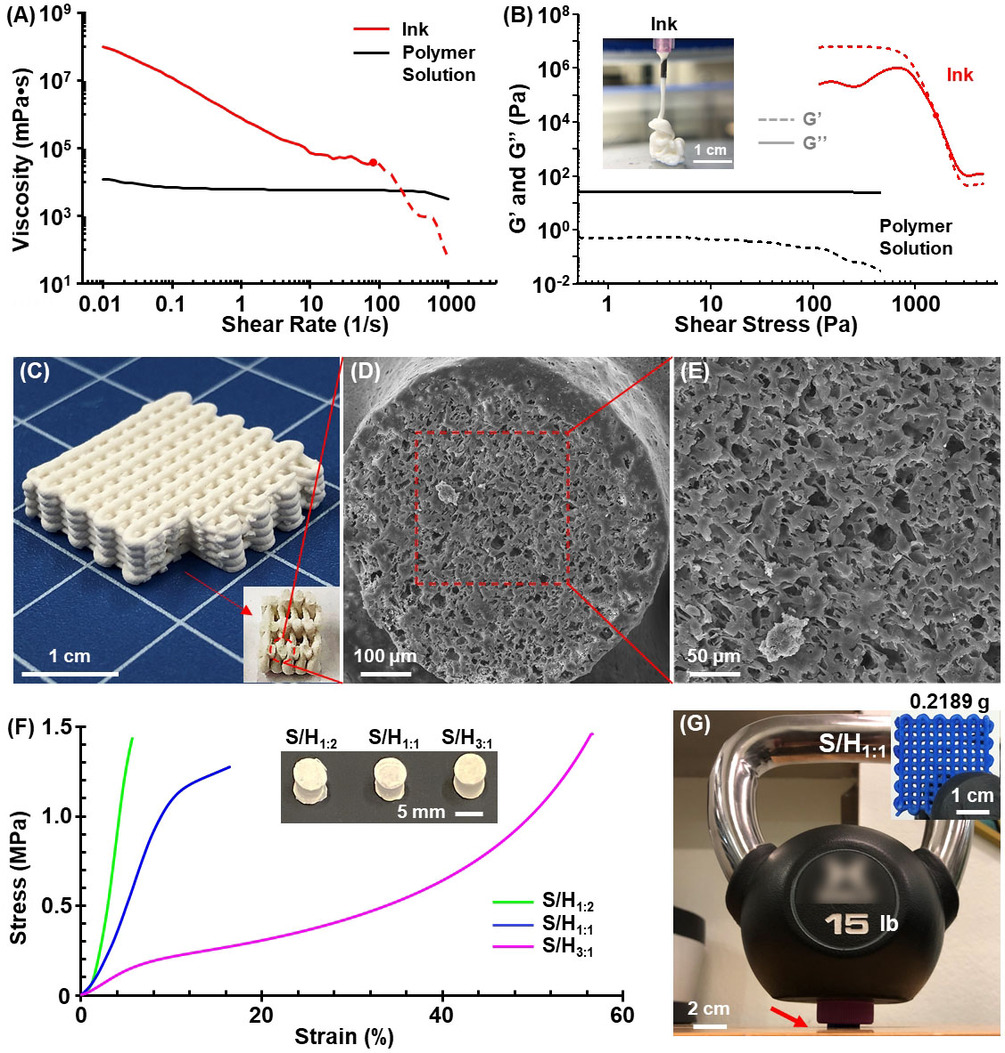
The research team has developed a means of fabricating plastics utilizing NaCl salt crystals and CO2 in the printing ink, that form soluble parts of the main part structure, that dissolve when washed in water, leaving microscopic pores all over the structure. The pores increase the surface area of the part, permitting faster degradation.
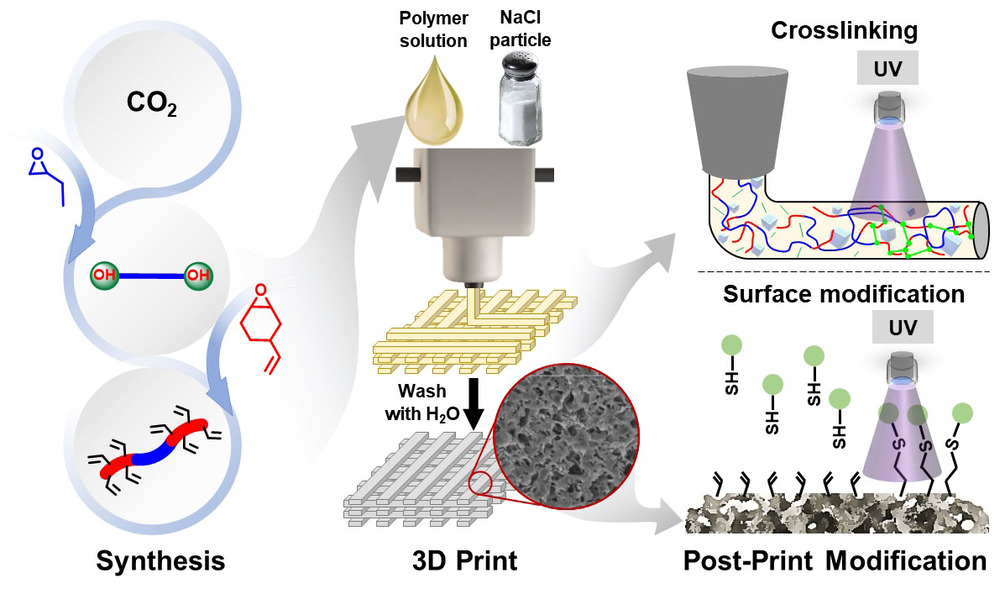
The polymers are prepared using a binary catalyst system and a chain transfer agent, providing a one-pot, two-step strategy to tailor the thermal and mechanical properties of the polymer. The alkene pendant groups on the polymer backbone can also be further modified with UV-induced thiol-ene surface functionalization and crosslinking to give objects with high solvent resistance and selective degradability.
“Our goal was to create sustainable degradable polymeric structures,” said Dr. Emily Pentzer, associate professor at Texas A&M University.
“We did this by leveraging the microstructures afforded by chemistry in conjunction with the macrostructures afforded by 3D printing.”
“Under the right conditions, the polymers we’ve created will actually degrade quickly. Ideally, they’ll break apart into small molecules that are not toxic. These smaller molecules won’t be able to carry things like heavy metals or bacteria.”
The end result was a plastic that had a smooth surface finish, but with microscopic pores that allow faster degradation. So while the polymer chains will still remain, the larger structure will no longer be existing to carry these other foreign elements.
The end-use applications include degradable food packaging, and a range of biomedical applications. In particular this makes the plastic suitable for implants and scaffolds that can degrade in the body.
The paper, titled “3D Printed CO2-Based Triblock Copolymers and Post-Printing Modification” has been published in the international version of German chemistry journal Angewandte Chemie, and is available for your perusal at this link.

